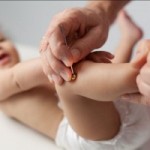
Shonishin. Japanese Acupuncture for children
For most of us the idea of putting needles in children for any reason would be something we would rather not do.
So as Acupuncture is a treatment method which uses needles to treat illness or disharmony in the body, I am often asked if it can be used on children. The answer is yes it can, but for obvious reasons children automatically associate the needles with pain, which upsets them, and in turn upsets us the parents/adults.
But there is a way of treating children as young as a few weeks old, using Oriental Medical techniques. The technique is called “Shonishin”, and it is a Japanese treatment method especially for children. Shonishin uses methods of stroking, tapping and scraping with special non invasive tools along the acupuncture meridians,both back and front, from head to toe instead of using acupuncture needles. It literally means “no needles”.
The theory is that childrens energy or “Qi” is so vibrant and new, that the balancing required when treating adults and thus necessitating acupuncture needles is not required. Because of their “newness”, children respond to treatment much quicker than adults, and quite often only a few sessions is required. Add onto this a childs love of being touched and stroked, and overall it leads to a very enjoyable experience for the child. Absolutely no tears! (It is always advisable that a parent or guardian is present).
So what can Shonishin treat?
It is especially good for:
Asthma, Allergies (including Hayfever), Anxiety, Constipation, Crying, Colic, Cough, Behavioural problems, Sleep disturbance, Sinusitis, Skin problems such as Exzema or Psoriasis, and other signs of stress.
For more information, please give me a call. Mairead Fahy, 0539483155 or 0876452409. info@bodymatters.ie